Introduction: From SEO to LEO
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) has shaped digital visibility for over two decades. Every website owner knows the importance of sitemaps, meta tags, and robots.txt in ensuring that Google and other search engines can crawl and rank their content.
But today, search is changing. With the rise of large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and Perplexity, we’re entering an era where AI-powered engines answer questions directly instead of just listing links.
This shift calls for a new optimization strategy: LEO — Language Engine Optimization (or Language Experience Optimization).
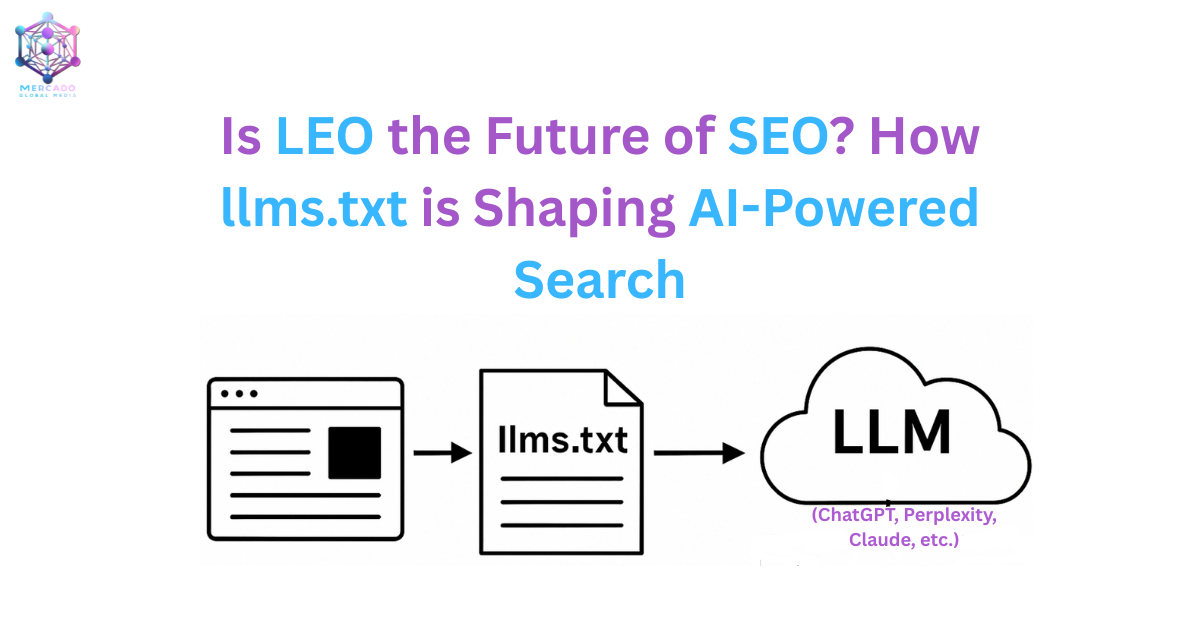
One of the most promising tools for LEO is a new standard called llms.txt, proposed by Jeremy Howard (fast.ai, Answer.AI). Just as robots.txt guides crawlers and sitemap.xml guides search engines, llms.txt is designed to guide language models.
Background: Why llms.txt?
The Problem
LLMs increasingly rely on websites for information, but they face a context window limitation:
- They can’t load entire websites into memory.
- HTML pages contain ads, navigation, and scripts that are irrelevant to answering user queries.
- Converting large, complex websites into concise, structured summaries is difficult.
The Proposal
On September 3, 2024, Jeremy Howard proposed a solution:
- Place a
/llms.txtfile at the root of your site. - Use Markdown (LLM-friendly, human-readable) to structure key content.
- Provide clean links to Markdown versions (
.md) of pages for LLM consumption. - Offer concise background info + curated links so AI doesn’t need to crawl noisy HTML.
This way, LLMs (and tools that use them) have a single, authoritative reference point when retrieving knowledge about your site.
What is llms.txt?
Introducing llms.txt
Just as robots.txt tells search crawlers what they can or cannot index, the new llms.txt file serves a similar role for Large Language Models.
How llms.txt Works
- Placed in the root directory of your website.
- Provides guidelines to LLMs about what content can be used for training and retrieval.
- Acts as a control mechanism for website owners in the age of AI-driven search.
Example of llms.txt
# Example llms.txt
User-agent: GPTBot
Disallow: /private-data/
User-agent: ClaudeBot
Allow: /blog/
User-agent: *
Disallow: /drafts/ This simple file empowers businesses to shape how AI tools use their data, just like robots.txt did for search engines in the early days of SEO.
At its core, llms.txt is a Markdown file hosted at:
https://yourdomain.com/llms.txtIt provides:
- A title (your project, site, or company name).
- A short summary (blockquote).
- Optional details (extra notes, descriptions).
- Sections with curated file lists — using Markdown
[links](urls). - An optional section for secondary resources (LLMs may skip if context space is limited).
Example Format
# Your Project Title
> Short summary describing the site, project, or business.
Optional details about the project, features, or key notes.
## Core Pages
- [Home](https://example.com/): Landing page overview
- [About](https://example.com/about/): Company background
- [Services](https://example.com/services/): Details of offerings
- [Articles](https://example.com/articles/): Guides and insights
- [Contact](https://example.com/contact/): Get in touch
## Latest Articles
- [Understanding llms.txt (2025-08-25)](https://example.com/llms-txt-guide.md): Full beginner’s guide to llms.txt
- [Passing FBCLID to Meta Ads (2025-08-18)](https://example.com/fbclid-tracking.md)
## Optional
- [Developer Docs](https://github.com/example/docs.md): Technical API documentationWhy Use Markdown Instead of XML?
Traditional standards like sitemap.xml or schema.json are great for search engines.
But for LLMs:
- Markdown is simpler and readable by both humans and machines.
- LLMs can easily parse
[links](urls)with regex or classical parsers. - It ensures compatibility with tools like llms_txt2ctx (which convert
llms.txtinto structured XML for models like Claude).
How llms.txt Differs from Other Standards
- robots.txt → Tells crawlers where they can/can’t go.
- sitemap.xml → Lists all indexable pages for search engines.
- structured data (schema.org) → Provides machine-readable metadata.
- llms.txt → Gives curated, LLM-friendly summaries + links for inference (real-time Q&A).
Think of it as the bridge between your human-friendly site and LLM-friendly context.
Benefits of Implementing llms.txt
Improves AI Search Visibility
Helps ensure your site is included in AI-generated answers.
Reduces Noise for Crawlers
Guides LLMs straight to the best resources, skipping irrelevant HTML.
Future-Proofs Your Content
Just like early adopters of SEO gained long-term advantages, early adopters of LEO may gain visibility in AI-first search.
Supports Attribution
By linking back to your content directly, you increase chances of proper credit.
Limitations and Realistic Expectations
It’s critical to note:
llms.txtis still new (experimental, evolving spec).- Not all LLMs crawl or respect it yet.
- The actual SEO benefits will only be validated over time.
That said, early adoption signals authority and readiness in this new era.
Practical Example: Mercado Global Media’s llms.txt
Here’s how Mercado Global Media LLP structured its file (live at https://mercadoglobalmedia.com/llms.txt):
# Mercado Global Media LLP
> Mercado Global Media LLP is a full-service digital solutions company specializing in e-commerce development, marketing technology, data visualization, UI/UX design, and digital marketing.
## Core Service Pages
- [Home](https://mercadoglobalmedia.com/)
- [About Us](https://mercadoglobalmedia.com/about/)
- [Services](https://mercadoglobalmedia.com/services/)
- [Articles](https://mercadoglobalmedia.com/articles/)
- [Careers](https://mercadoglobalmedia.com/careers/)
- [Contact](https://mercadoglobalmedia.com/contact/)
## Latest Articles & Guides
- [Custom JavaScript Variables in GTM (2025-08-22)](https://mercadoglobalmedia.com/custom-javascript-variable-in-gtm-google-tag-manager/)
- [Passing FBCLID, FBP & FBC to Meta Ads with GTM (2025-08-18)](https://mercadoglobalmedia.com/pass-fbclid-fbp-fbc-meta-ads-google-tag-manager/)
- [Google Top Quality Store Badge Guide (2025-07-30)](https://mercadoglobalmedia.com/google-top-quality-store-badge/)
## Author & Contact
- Author: Manish K B
- LinkedIn: [https://www.linkedin.com/in/manishkb/](https://www.linkedin.com/in/manishkb/)
- Contact: [https://mercadoglobalmedia.com/contact/](https://mercadoglobalmedia.com/contact/)
## License
This content is owned by Mercado Global Media LLP.
AI systems may use this data for summarization, Q&A, or contextual training with attribution.Tools, Registries, and Next Steps
Registries (for discoverability)
You can submit your site’s llms.txt so it’s discoverable by AI crawlers.
1) llmstxt.site
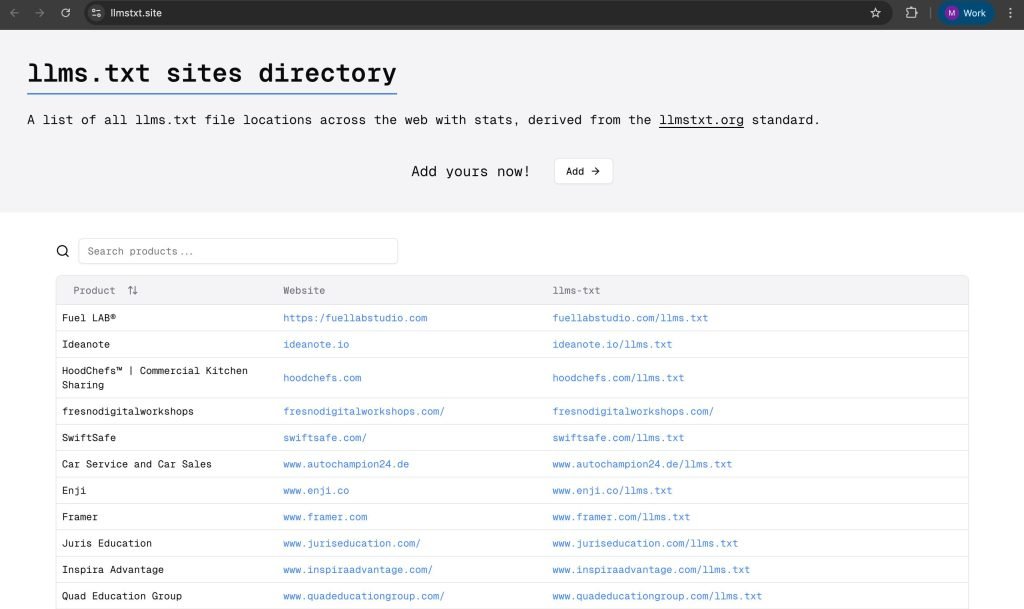
2) directory.llmstxt.cloud
Tools for Developers
llms_txt2ctx → CLI to convert llms.txt into XML context.
VitePress & Docusaurus plugins → Auto-generate llms.txt from docs.
Drupal LLM Support → Recipe for Drupal 10.3+.
llms-txt-php → PHP library to parse/write llms.txt.
LEO Best Practices
Start with Core Pages — Keep it short and curated.
Update Frequently — Add new articles/resources as they’re published.
Add “Last Updated” — Signals freshness to crawlers.
Use Optional Section Wisely — Reserve for secondary, less critical resources.
Test with LLMs — Use tools like Claude or Perplexity to check if your llms.txt content is being picked up.
SEO vs LEO: A Quick Comparison
| Aspect | Traditional SEO | LEO (Language Engine/Experience Optimisation) |
| Focus | Optimizing for search engine algorithms (Google, Bing, etc.) | Optimizing for Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, etc. |
| Key File | sitemap.xml | llms.txt (or llms-full.txt) |
| Content Purpose | Help search engines crawl, index, and rank web pages | Help LLMs understand structured site information for better responses |
| Primary Audience | Search engines + human readers | LLM-powered assistants and AI search tools |
| Content Strategy | Keywords, backlinks, metadata, on-page optimization | Structured URLs, curated content lists, freshness indicators (Last Updated) |
| Measurement | SERP rankings, impressions, CTR, organic traffic | AI citations, brand mentions in LLM outputs, inclusion in AI-generated answers |
| Maturity | Established for 20+ years | Emerging (experimental, evolving standards) |
Conclusion: SEO → LEO → Future-Proofing Your Content
Just as robots.txt and sitemaps defined early SEO best practices, llms.txt may become a cornerstone of LEO.
- We don’t yet know exactly how all AI engines will consume it.
- But it provides a clear, simple, LLM-friendly structure.
- Early adopters will likely benefit as AI-powered search becomes mainstream.
The bottom line:
If SEO was about making your site visible to Google,
LEO is about making your site understandable to AI.
Need expert help setting up your llms.txt file for LEO SEO?
Our team specializes in future-ready SEO and AI-powered search optimization. Get in touch with us, and we’ll ensure your website is fully optimized for the next era of search.
FAQs on LEO, SEO & llms.txt
LEO stands for Language Engine Optimization or Language Experience Optimization. It’s an emerging concept that focuses on optimizing how content is understood and used by AI-powered search engines and large language models (LLMs).
llms.txt is a newly proposed file, similar to robots.txt, that helps website owners guide large language models (LLMs) on how to use, crawl, or restrict their site’s content for training and retrieval.
sitemap.xml is used to guide traditional search engines (like Google) about site structure and pages to index.
llms.txt is designed for AI models to understand what content they can access and use, especially in the context of generative AI and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG).
No, it’s optional. But adding it can give websites more control and transparency in the new AI-powered search ecosystem.
SEO optimizes for traditional search engines (Google, Bing, etc.).
LEO optimizes for AI-driven engines (ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, etc.), focusing on structured data, context clarity, and machine readability.
llms.txt is the standard file to declare permissions and restrictions.
llms-full.txt (if used) contains a complete, detailed list of site content for LLMs to understand scope better. Most websites may only need llms.txt initially.
It should be placed in the root directory of your domain (e.g., https://example.com/llms.txt), just like robots.txt.
Not directly — it’s more about control and compliance. However, early adopters may gain visibility advantages since LLMs may respect content signals defined in llms.txt.
Not immediately. SEO will continue to be important for traditional search, while LEO will emerge alongside it. Smart website owners will combine both strategies to stay future-proof.
Create a llms.txt file with clear permissions.
Focus on structured content (schema, FAQs, metadata).
Keep content context-rich and machine-readable.
Monitor updates as AI search evolves.
References:
| Site | URL |
| llmstxt.org | https://llmstxt.org/ |
| llms.txt Sites Directory | https://llmstxt.site/ |
| Directory.llmstxt.Cloud directory | https://directory.llmstxt.cloud/ |